To install Windows updates using PowerShell, you can utilize the `Install-WindowsUpdate` command from the PSWindowsUpdate module, which simplifies the update process.
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
Understanding PowerShell and Windows Updates
What is PowerShell?
PowerShell is a powerful scripting language and command-line shell designed for system and network administration. It allows users to automate tasks and control the system through a series of commands and scripts. With its ability to handle a wide variety of system management tasks, it has become an essential tool for IT professionals and system administrators alike.
The Role of PowerShell in Windows Operating Systems
PowerShell interacts deeply with the Windows operating system, providing access to system management tasks that can be executed directly from the command line or through scripts. This includes everything from file management to user management and, notably, updating the operating system itself. By harnessing the power of PowerShell, administrators can efficiently manage and maintain the systems in their purview.
Why Use PowerShell for Windows Updates?
There are several compelling reasons to utilize PowerShell for managing updates:
- Automation Capabilities: PowerShell allows you to automate the process of checking for and installing updates, saving you time and effort.
- Remote Management: You can execute update commands on remote machines, which is especially useful in larger environments.
- Scriptability and Flexibility: PowerShell scripts can be customized to suit specific needs, enabling tailored update approaches that align with organizational policies.
Preparing Your Environment
Ensuring PowerShell is Installed
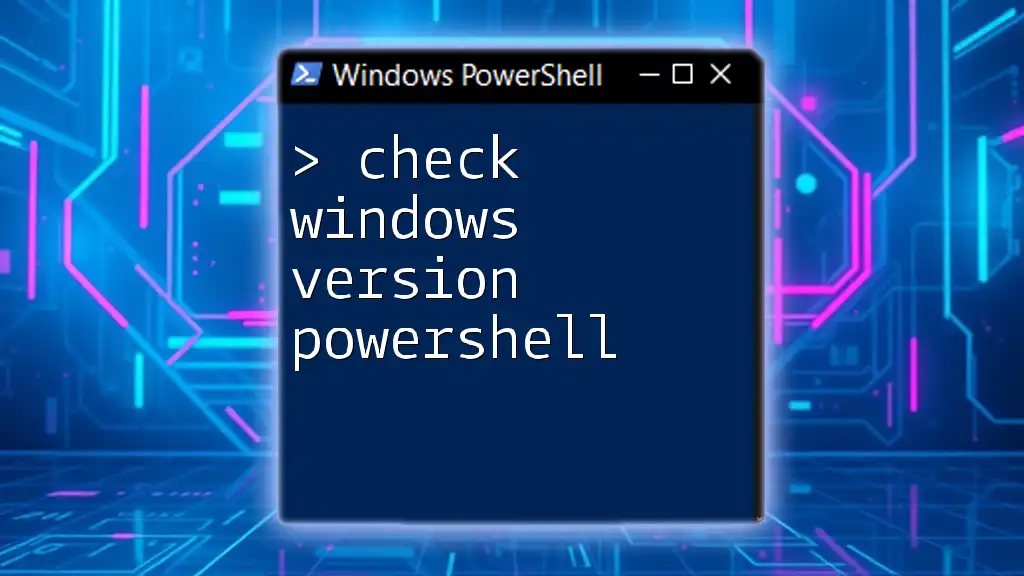
To start, you must ensure that PowerShell is installed on your Windows system. Depending on your version of Windows, either Windows PowerShell or PowerShell Core is available. To check your installed version, you can run the following command:
$PSVersionTable.PSVersion
Knowing your PowerShell version helps you understand which features and modules you can use.
Running PowerShell as Administrator
For most update commands, running PowerShell with elevated privileges is necessary. Here's how you can launch an elevated session:
- Open the Start menu, type "PowerShell."
- Right-click on the Windows PowerShell option and select "Run as administrator."
This step is critical because many update commands require administrative access to make changes to the operating system.
Using PowerShell to Manage Windows Updates
Understanding Update Modules
PowerShell's capability to manage Windows updates relies on specific modules, particularly the `PSWindowsUpdate` module. This module enhances PowerShell's functionality for handling Windows updates seamlessly. To use it, you must install it first:
Install-Module -Name PSWindowsUpdate -Force
After installation, you can take advantage of various commands that streamline the update process.
Checking for Available Updates
Before installing updates, it’s essential to know what updates are available. You can execute the following command to list all pending updates:
Get-WindowsUpdate
This command provides a detailed list of available updates, including their titles, KB article IDs, and installation statuses. Understanding this output allows administrators to plan updates effectively.
Installing Windows Updates
Installing All Available Updates
If you wish to install all pending updates quickly, execute the following command:
Install-WindowsUpdate -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
This command installs all available updates while automatically accepting the prompts and rebooting the system as needed. This is an ideal method for keeping systems up to date with minimal manual intervention.
Installing Specific Updates
In some cases, you may want to install a particular update, such as a critical security patch. To do this, first, locate the update ID (KB Article ID) from the previous list, then run:
Install-WindowsUpdate -KBArticleID "KB123456"
Replace `"KB123456"` with the actual KB number of the update. This targeted approach allows you to manage specific updates without affecting others.
Monitoring Update Installation
After installing updates, you'll want to verify that the process completed successfully. You can check the status by looking at the Windows Update logs with the following command:
Get-WindowsUpdateLog
This command produces logs that outline what updates were installed and any errors that may have occurred during installation, facilitating troubleshooting when necessary.
Automating Windows Update Installation
Creating PowerShell Scripts for Regular Updates
PowerShell scripts can streamline the update process even further. A basic automated script for updating Windows might look like this:
# Example script to update Windows
Import-Module PSWindowsUpdate
Get-WindowsUpdate -Install -AcceptAll -AutoReboot
This script imports the necessary module and performs an installation of all updates, accepting any prompts and rebooting the system if required. Using scripts like this makes regular updates simple and consistent.
Scheduling Scripts with Task Scheduler
To ensure that updates are installed regularly without user intervention, you can schedule PowerShell scripts via the Windows Task Scheduler. Setting up a task involves selecting your script and configuring it to run at predefined intervals (e.g., daily, weekly). This is essential for maintaining a secure and up-to-date system environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
PowerShell Execution Policy
Sometimes, PowerShell scripts won't run due to the execution policy settings. The execution policy determines the conditions under which PowerShell loads configuration files and runs scripts. To check your current policy, run:
Get-ExecutionPolicy
If you need to run scripts, you might want to change the policy to allow script execution. This can be done with:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Always exercise caution and revert to a more restrictive policy if your security requirements demand this.
Handling Errors During Update Installation
In the event that you encounter errors while using PowerShell to install updates, common error messages include connectivity issues, authentication problems, or conflicts with existing software. It's wise to document each error and consult the logs generated by the `Get-WindowsUpdateLog` command for deeper insight into the root cause.
Best Practices for Using PowerShell to Manage Updates
- Regularly Updating PowerShell and Modules: Keeping your PowerShell version and its modules up to date ensures you have the latest features and security patches.
- Keeping Security in Mind: When creating and running scripts, be mindful of security implications, especially when executing commands that require elevated privileges.
- Documenting Update Processes: As you establish procedures for updating systems, document them thoroughly to promote consistency and knowledge retention within your team.
Conclusion
Managing Windows updates with PowerShell offers an efficient and powerful method for ensuring that your systems remain secure and up to date. By embracing the capabilities of PowerShell, IT professionals can automate and streamline their update processes significantly. Encourage exploration of PowerShell's features and consider integrating these practices into your organizational workflows for optimal results.
Additional Resources
To further enhance your PowerShell knowledge, refer to the official Microsoft documentation and recommended learning platforms or books. These resources can provide in-depth insights and real-world applications of PowerShell for managing Windows updates and beyond.
Call to Action
If you found this guide helpful, subscribe for more tips and tricks related to PowerShell! Stay tuned for upcoming workshops and webinars designed to elevate your PowerShell skills to the next level.