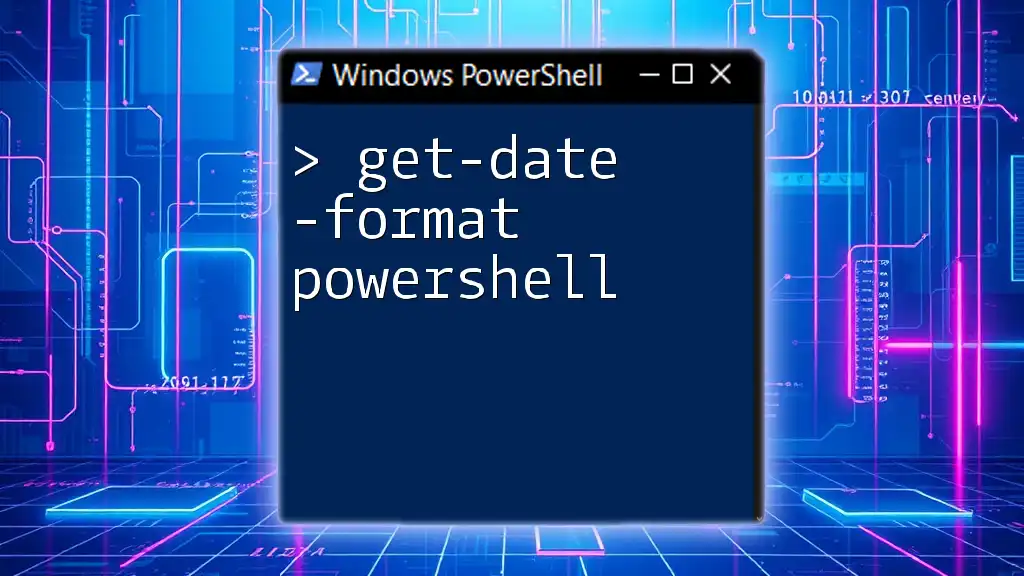
The `Get-Date -Format` command in PowerShell allows you to retrieve the current date and time in a specified format, offering flexibility in how you present date information.
Here's a code snippet demonstrating its usage:
Get-Date -Format "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
Understanding `Get-Date`
What is `Get-Date`?
The `Get-Date` cmdlet is a built-in PowerShell command that retrieves the current date and time from the system. By default, the output appears in a long date format, which includes both the date and the time. This cmdlet is essential for various scripting tasks, enabling users to manipulate and display date and time information effectively.
Basic Syntax
The basic syntax for using `Get-Date` is easy to grasp. The command can be run simply by typing:
Get-Date
This command will display the current date and time in your system's default format.
Using the `-Format` Parameter
Introduction to the `-Format` Parameter
The `-Format` parameter allows you to customize the output of the `Get-Date` cmdlet significantly. By specifying a format string, you can tailor how the date and time are presented, whether you need a short date format, a long date format, or a completely bespoke arrangement. This flexibility is crucial for enhancing the readability of scripts, reports, and logs.
Common Formatting Strings
Standard Date and Time Formats
PowerShell provides several built-in standard formats that are quite useful.
-
Short date: This format displays the date in a compact manner. For example:
Get-Date -Format "d"This command will output something like `09/22/2023`.
-
Long date: To display the full name of the day and month:
Get-Date -Format "D"This will produce an output like `Friday, September 22, 2023`.
Custom Date and Time Formats
The true power of `get-date -format powershell` shines through with custom format strings, where you can combine elements to create your desired output.
- Key components:
- Day: `d` (1 or 2 digits) or `dd` (2 digits)
- Month: `M` (1 or 2 digits) or `MM` (2 digits)
- Year: `y` (2 digits) or `yyyy` (4 digits)
- Hour: `h` (1-2 digits) or `hh` (2 digits)
- Minute: `m` (1 or 2 digits)
- Second: `s` (1 or 2 digits)
Utilizing these components, you can craft very specific formats based on your needs.
Formatting Examples
Using Standard Formats
Standard formats can be used quickly for commonly required outputs.
-
ISO 8601 format: This standardized format is often required in programming and data exchange. Running:
Get-Date -Format "yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss"will produce a result like `2023-09-22T15:30:45`.
-
Short date format: To get the current date in a concise manner:
Get-Date -Format "d"The output will resemble `9/22/2023`.
Custom Date Formats
Creating tailored formats can be done with ease. For example:
-
US date format: If you want the date displayed in the MM/DD/YYYY format, use:
Get-Date -Format "MM/dd/yyyy"This will yield `09/22/2023`.
-
Full custom format: To create a more descriptive date and time string:
Get-Date -Format "dddd, MMMM dd, yyyy HH:mm:ss"This results in something like `Friday, September 22, 2023 15:30:45`.
Practical Applications of Get-Date Formatting
Date for Filenames
A practical application of date formatting is generating timestamps for filenames. This is especially useful for logging and documentation tasks where unique file names are necessary.
For example, to create a timestamped filename, you could use the following command:
$timestamp = Get-Date -Format "yyyyMMdd_HHmmss"
The `$timestamp` variable now contains a string like `20230922_153045`, which can be easily appended to your filenames.
Date in Reports
Another common use case involves inserting formatted dates into reports. For instance, to generate a header for a report that includes the current date, you might execute:
$header = "Report generated on: " + (Get-Date -Format "MMMM dd, yyyy")
This will produce a header such as `Report generated on: September 22, 2023`.
Additional Tips for Using `Get-Date`
Localization and Cultural Formatting
Understanding localization options can broaden the applicability of your scripts. PowerShell allows for culture-specific formatting, which is especially useful when scripts are shared across different regions.
For example, to output the date accordingly for the German culture, you can run:
Get-Date -Format "D" -UFormat "%A, %d. %B %Y" -Culture "de-DE"
This would yield a result like `Freitag, 22. September 2023`.
Combining with Other Cmdlets
The `Get-Date` cmdlet works seamlessly with other cmdlets, amplifying its utility. For instance, consider using it with `Where-Object` to filter objects by date. For example:
Get-EventLog -LogName System | Where-Object { $_.TimeGenerated -ge (Get-Date).AddDays(-7) }
This command retrieves system events from the last seven days, illustrating how `Get-Date` can dynamically impact data handling.

Troubleshooting Common Issues
Formatting Errors
When formatting strings, mistakes can happen. Common errors include using incorrect format specifiers or mismatched quotes. Pay attention to the exact string syntax and consult PowerShell's documentation if you're unsure.
Performance Considerations
While `Get-Date` is efficient, using it in performance-critical scripts may warrant some caution. Frequent calls to `Get-Date` can slow down the execution of long-running tasks. Consider storing the date in a variable if you need to reference it multiple times:
$currentDate = Get-Date
# Use $currentDate in subsequent calls

Conclusion
Mastering `get-date -format powershell` opens up a wealth of possibilities for date and time manipulation within your PowerShell scripts. By understanding the various format options and practical applications, you can increase the clarity and utility of your scripts, enhancing readability and functionality. Experiment with different formatting styles to suit your needs and strive to leverage this powerful cmdlet for your automation tasks. Happy scripting!

Additional Resources
For further learning and exploration, consult the official Microsoft documentation on `Get-Date`, browse recommended PowerShell books, and consider joining PowerShell community forums. These resources will provide additional guidance and support as you continue your journey with PowerShell.